Introduction:
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, cybersecurity has become an essential concern for both individuals and businesses. The increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber threats highlight the importance of adopting robust security measures. By implementing cybersecurity best practices, individuals and organizations can minimize risks, protect sensitive data, and maintain trust in an ever-evolving technological environment.
- Password Management:
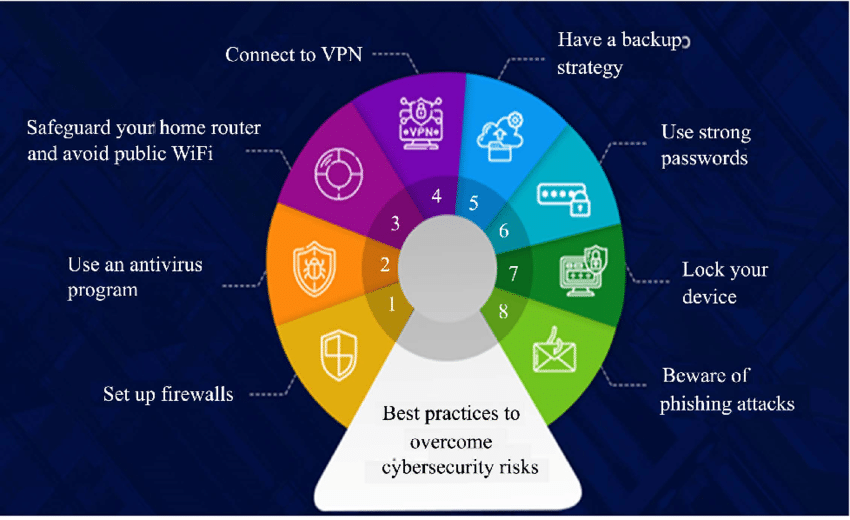
One of the fundamental aspects of cybersecurity is effective password management. Individuals and businesses should adopt strong, unique passwords for each online account. Passwords should be complex, incorporating a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters. Additionally, it is crucial to regularly update passwords and avoid using common phrases or personal information.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
Implementing two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring an additional verification step after entering a password. This method often involves a unique code sent to a registered mobile device or email address. Enabling 2FA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised.
- Regular Software Updates:
Software providers regularly release updates and patches to fix security vulnerabilities. Individuals and businesses must ensure that all devices, operating systems, and applications are up to date. Regularly installing updates protects against known security flaws and helps maintain the integrity of systems and data.
- Data Encryption:
Data encryption is vital in safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access. Employing encryption techniques ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable. Businesses should implement encryption protocols for both data in transit and at rest, while individuals can use encrypted messaging apps and secure cloud storage services.
- Employee Training and Awareness:
Educating employees about cybersecurity threats is crucial for maintaining a secure environment within organizations. Regular training sessions can cover topics such as phishing, social engineering, and safe browsing habits. Employees should be aware of the risks associated with opening suspicious emails or clicking on unfamiliar links to prevent malware infections.
- Regular Backups:
Data backups are essential for mitigating the impact of potential data breaches or system failures. Individuals and businesses should regularly back up critical data to offline or cloud storage, ensuring that a recent copy is available for recovery in case of an incident. Reliable backup solutions provide resilience against ransomware attacks and other forms of data loss.
- Network Security:
Implementing robust network security measures is vital for businesses. Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software should be in place to protect networks from unauthorized access and malware. Regular network monitoring and vulnerability assessments help identify potential weaknesses and allow for timely remediation.
- Secure Wi-Fi and Remote Access:
Individuals and businesses should secure their Wi-Fi networks by using strong passwords and enabling network encryption (WPA2/WPA3). Public Wi-Fi networks, often unsecured, should be used cautiously, avoiding sensitive transactions or sharing confidential information. When accessing networks remotely, individuals and employees should rely on secure Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to encrypt data transmission.
- Incident Response and Contingency Plans:
Preparing for cybersecurity incidents is as important as preventing them. Businesses should have an incident response plan in place to address potential breaches effectively. This plan should outline steps to contain, mitigate, and recover from security incidents, minimizing potential damages. Regularly testing and updating the plan ensures its effectiveness.
Conclusion:
Cybersecurity best practices are essential for protecting individuals and businesses from evolving cyber threats. By adopting these practices, individuals can enhance their personal digital security, while businesses can safeguard their data, systems, and reputation. Emphasizing strong password management, two-factor authentication, regular software updates, data encryption, employee training, backups, network security, secure Wi-Fi practices, and incident response planning can significantly reduce vulnerabilities and enhance overall cybersecurity posture. Prioritizing cybersecurity not only protects valuable information but also contributes to a safer and more secure digital world for everyone.